The 1.8-liter Toyota 2ZZ-GE engine was produced from 1999 to 2011 at the Japanese plant for both sports versions of popular civilian models and Lotus brand sports cars. The motor was created together with Yamaha engineers and equipped with a VVTL-i phase control system.
The ZZ family includes engines: 1ZZ‑FE, 1ZZ‑FED, 2ZZ‑GE, 3ZZ‑FE, 4ZZ-FE.
Specifications
| Production years | 1999-2011 |
| Displacement, cc | 1796 |
| Fuel system | MPI injector |
| Power output, hp | 164 – 190 (atmospheric version) 220 – 260 (supercharged version) |
| Torque output, Nm | 170 – 180 (atmospheric version) 215 – 235 (supercharged version) |
| Cylinder block | aluminum R4 |
| Block head | aluminum 16v |
| Cylinder bore, mm | 82 |
| Piston stroke, mm | 85 |
| Compression ratio | 11.5 |
| Features | no |
| Hydraulic lifters | no |
| Timing drive | chain |
| Phase regulator | VVT-i (atmospheric version) VVTL-i (supercharged version) |
| Turbocharging | no (atmospheric version) compressor (supercharged version) |
| Recommended engine oil | 5W-30 |
| Engine oil capacity, liter | 4.4 |
| Fuel type | petrol |
| Euro standards | EURO 3/4 |
| Fuel consumption, L/100 km (for Toyota Celica 2002) — city — highway — combined |
11.5 6.6 8.4 |
| Engine lifespan, km | ~200 000 |
| Weight, kg | 135 |
2ZZ-GE was installed on cars:
- Toyota Celica SS-II (Japan, 187 hp);
- Toyota Celica GT-S (USA, 180 hp);
- Toyota Celica 190/T-Sport (UK, 189 hp);
- Toyota Corolla Sportivo (Australia, 189 hp/180 Nm);
- Toyota Corolla TS (Europe, 189 hp);
- Toyota Corolla Compressor (Europe, turbocharged, 222 hp);
- Toyota Corolla XRS (USA, 164/170 hp);
- Toyota Corolla Fielder Z Aero Tourer (Japan, 196 hp);
- Toyota Corolla Runx Z Aero Tourer (Japan, 187 hp);
- Toyota Corolla RunX RSi (South Africa, 141 kW/180 Nm);
- Toyota Matrix XRS (USA, 164-180 hp);
- Pontiac Vibe GT (USA, 164-180 hp);
- WiLL VS 1.8;
- Lotus Elise (North America/UK, 190 hp);
- Lotus Exige (US/UK, 190hp NA and 243hp turbocharged);
- Lotus 2-Eleven (US/UK, turbocharged, 252 hp).
Frequent problems
- Oil burn. The most common problem with 2ZZ when passing the mark of 150 thousand kilometers. Decarbonization helps temporarily. As a result, a major overhaul or replacement of the motor cannot be avoided.
- Noises and knocks inside the motor. The main reason is a loose timing chain. Replacement required.
- Instability of revolutions. It is necessary to clean the valves at idle speed. Also, the reason may be in the throttle-valve module – diagnostics required.
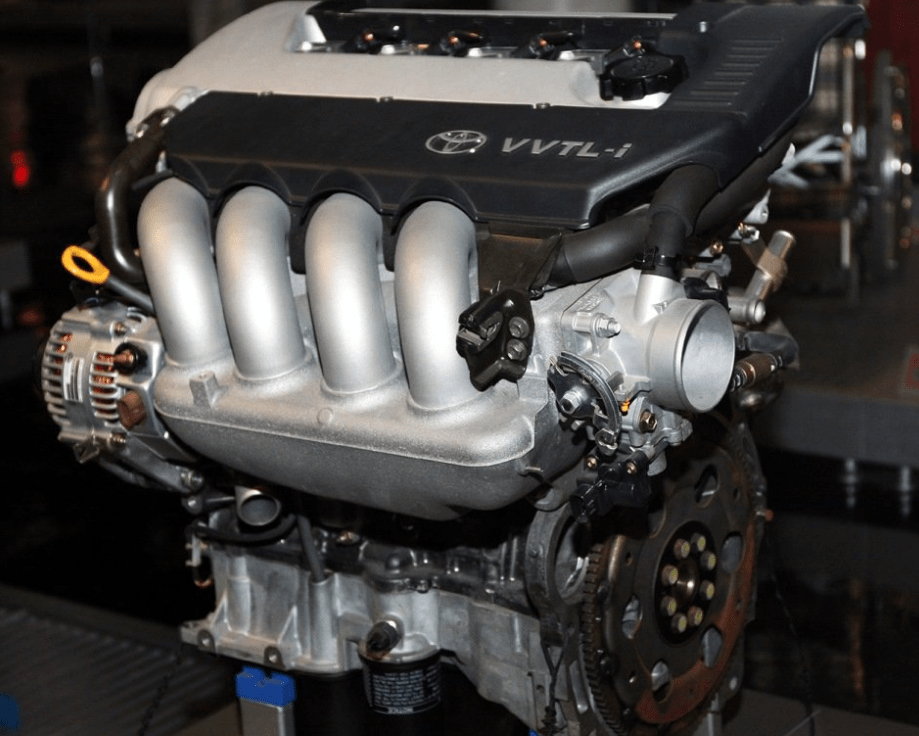
The periodic whims of the VVTL-i-system are added to the list of problems. For prophylaxis, after 50 thousand km of track, it is necessary to replace the lift bolts. If this is not done, the system may fail and, as a result, the power will drop over 6 thousand rpm. The durability of the motor does not exceed the same indicator 1ZZ, that is, no more than 200 thousand km. Alternatively, it can be replaced with 3S-GTE.
The main structural problem of the 2ZZ GE motor remains the ultra-small jumper between the cylinders:
- during the cooling of the aluminum cast block, the formation of shells, cavities is possible with a probability of more than 75%;
- aluminosilicate inclusions have a different cooling rate, microcracks form near them;
- during the curing process, a porous structure is possible, again due to foreign inclusions of aluminosilicate.
Such an internal combustion engine device is initially prone to liner scuffing. The mesh of the hone (special coating of the inner wall of the sleeve) is wrinkled, unlike a similar coating of a steel or aluminum sleeve. The manufacturer declared the resource of the sleeves to be sufficient, but did not ensure this in practice.
All of the above is true for the piston, since this part is manufactured using a similar technology. The hardness of the piston skirt is increased by applying phosphorus-containing and iron-containing coatings.
Through long tests, the manufacturer managed to achieve wear of the piston rings, and not the liners in this friction pair, to slightly increase the maintainability of the cylinder-piston group.






